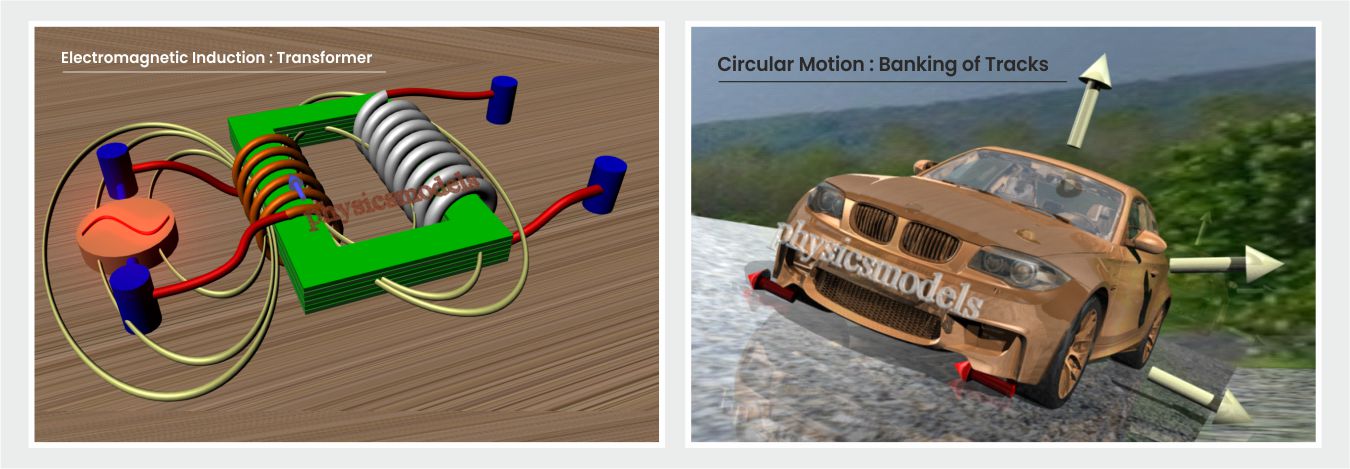
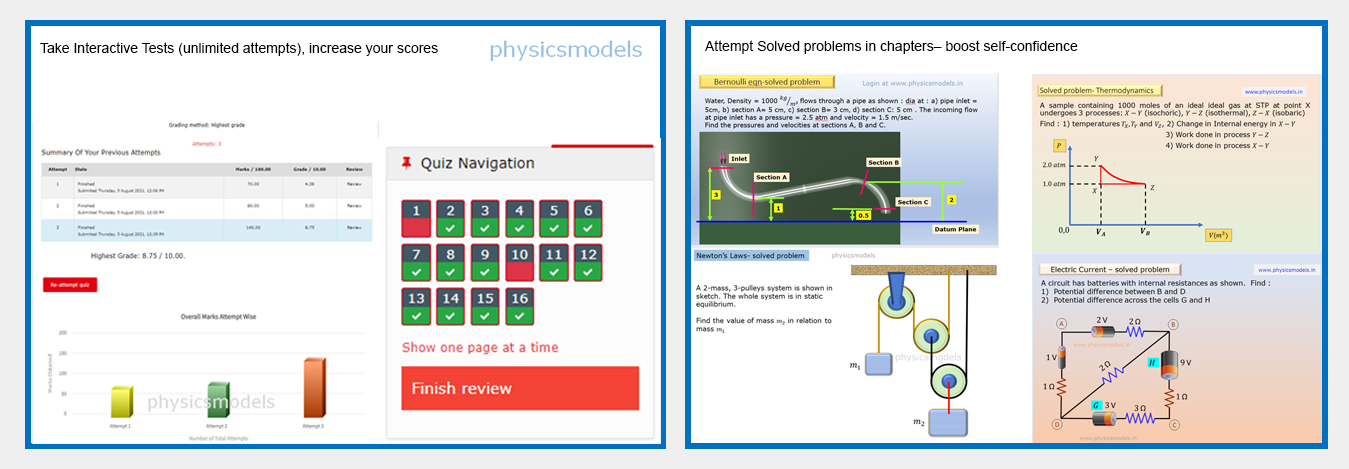
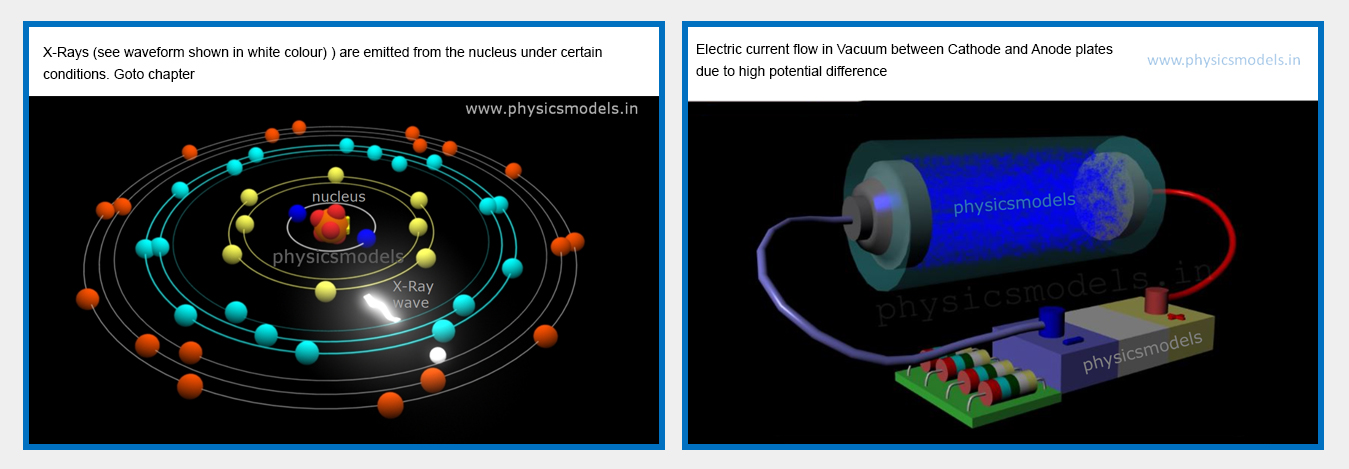
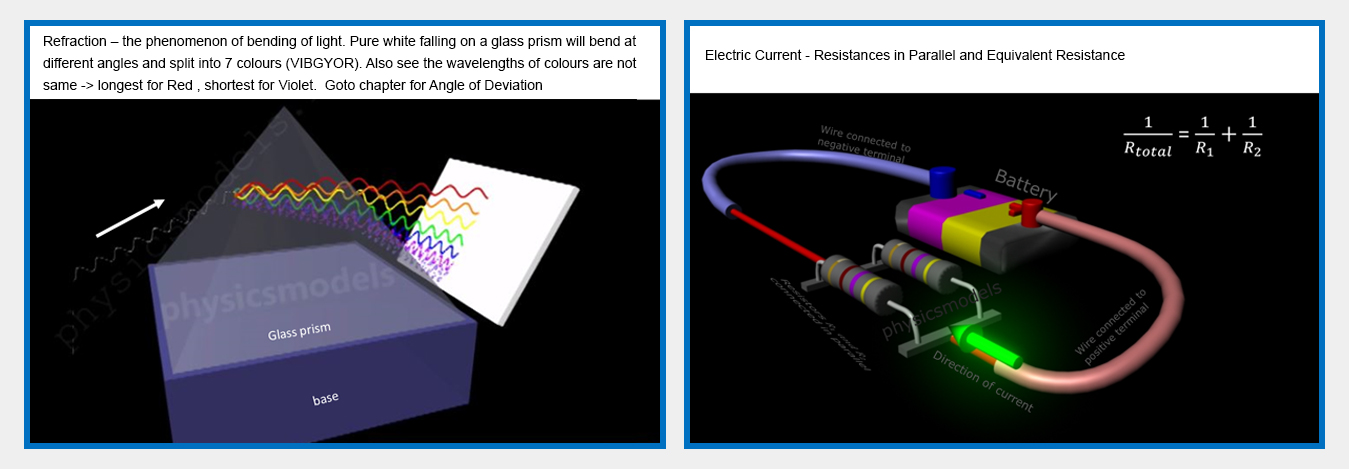
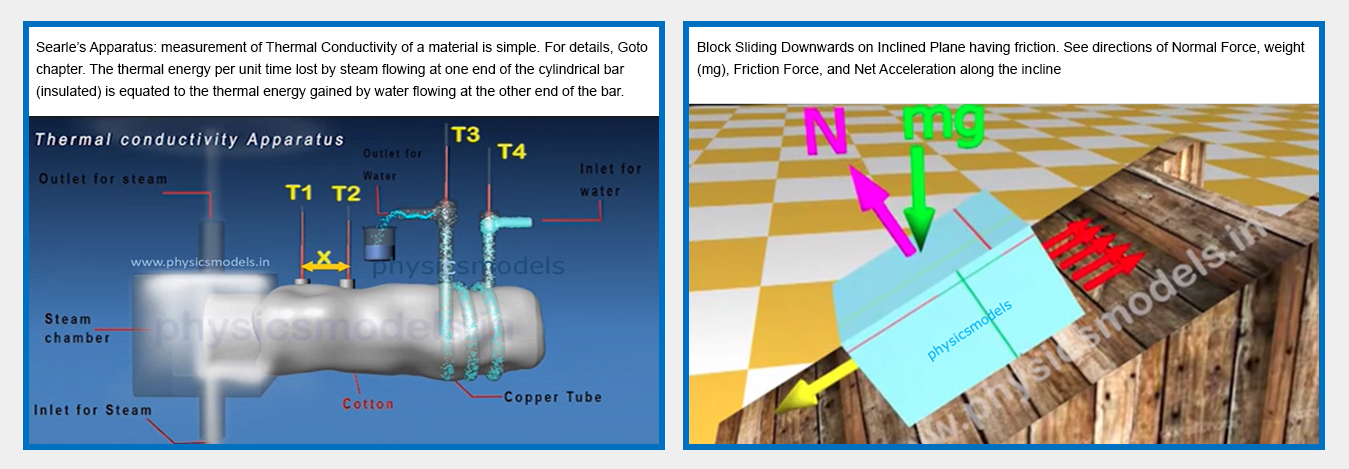
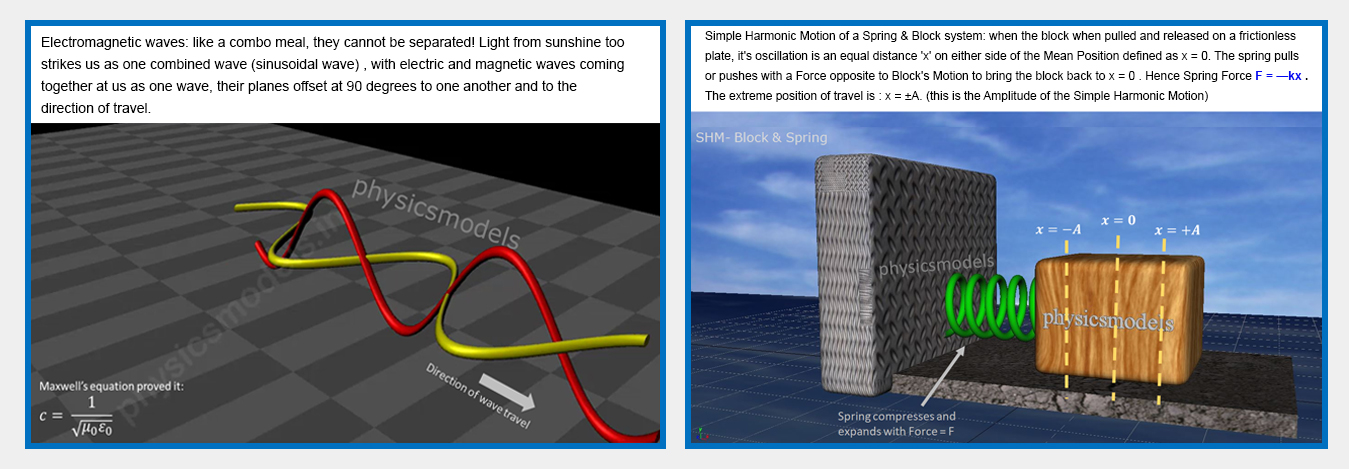
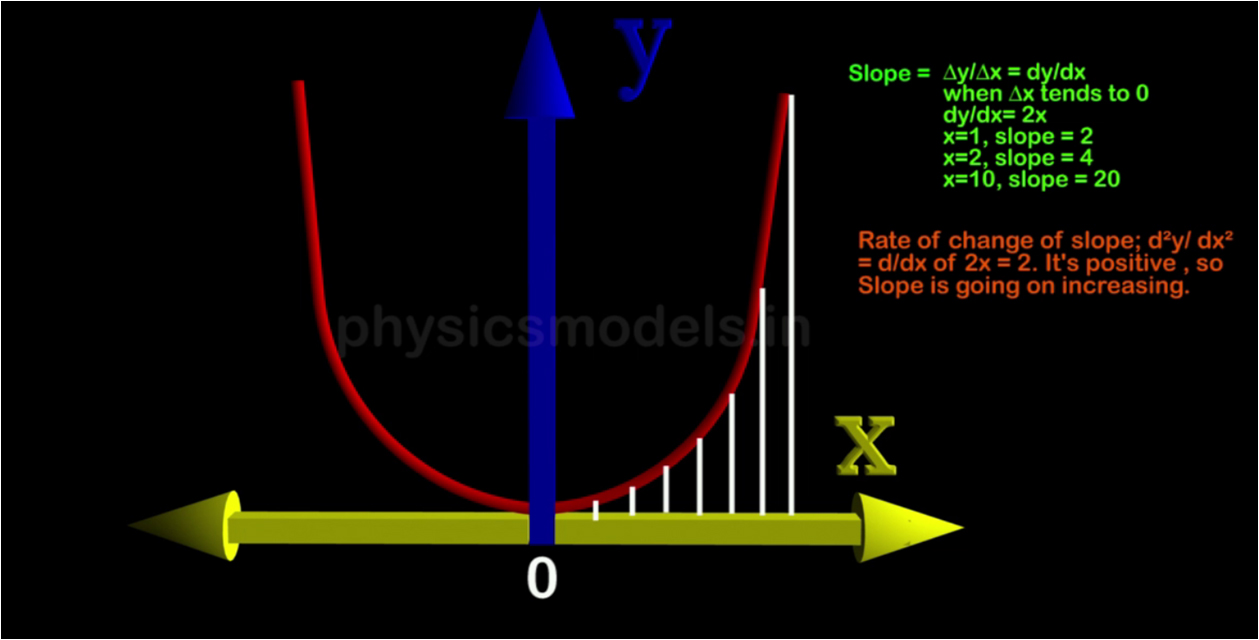
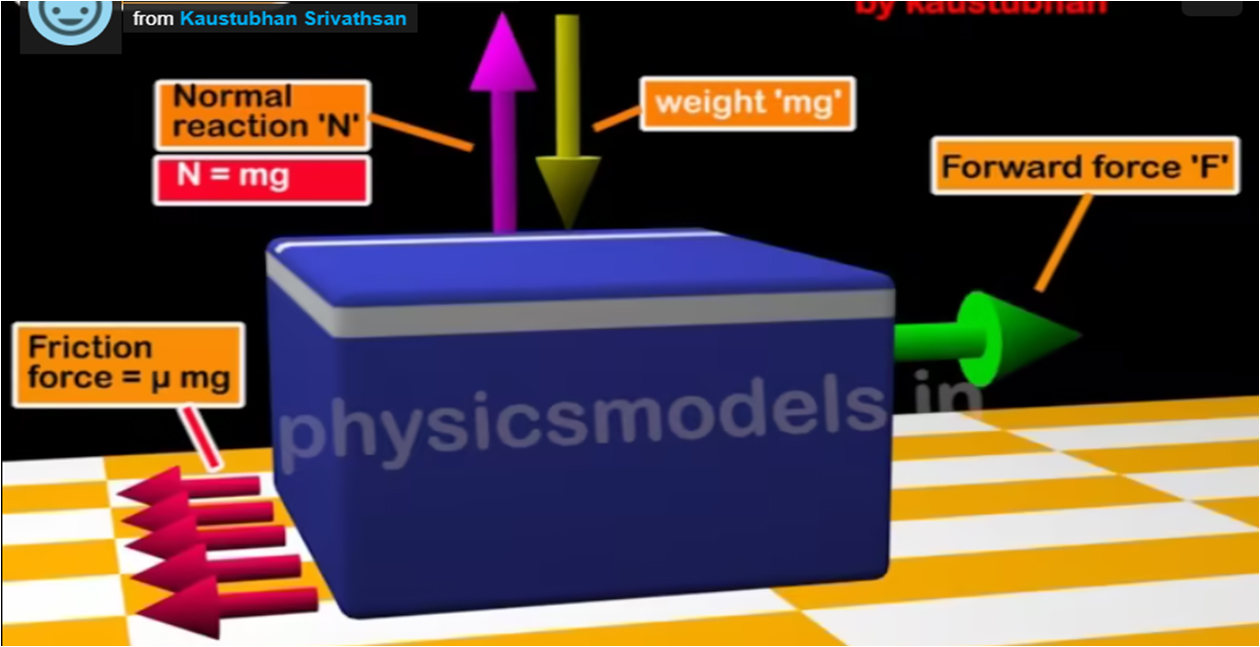
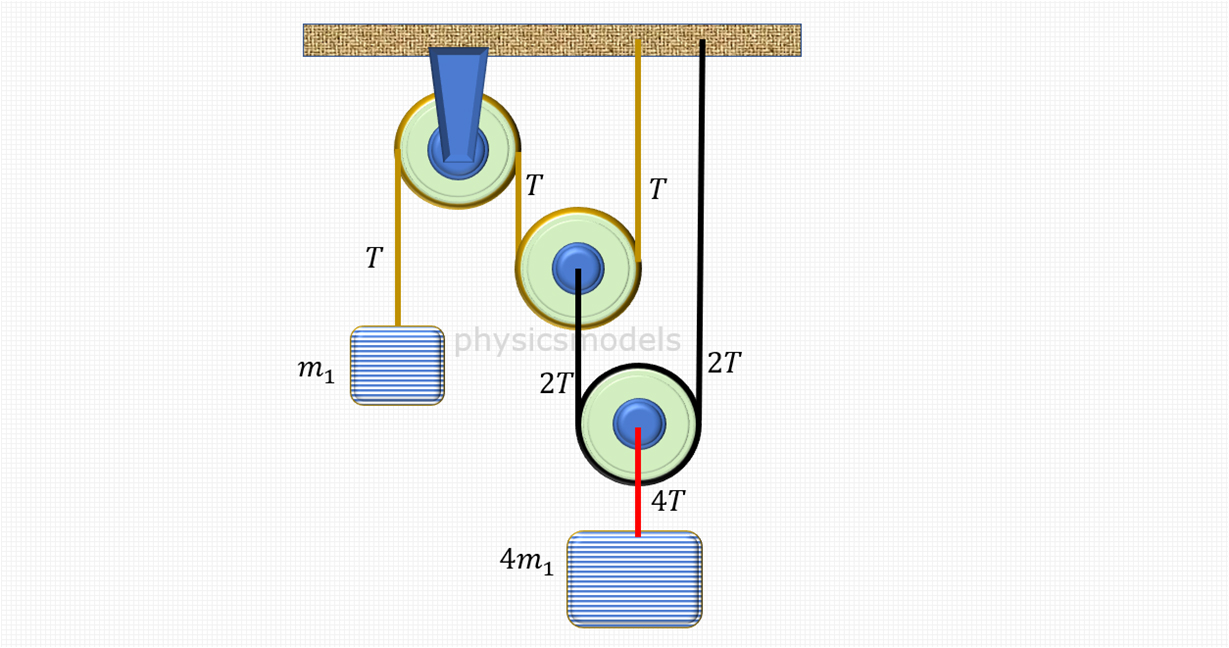
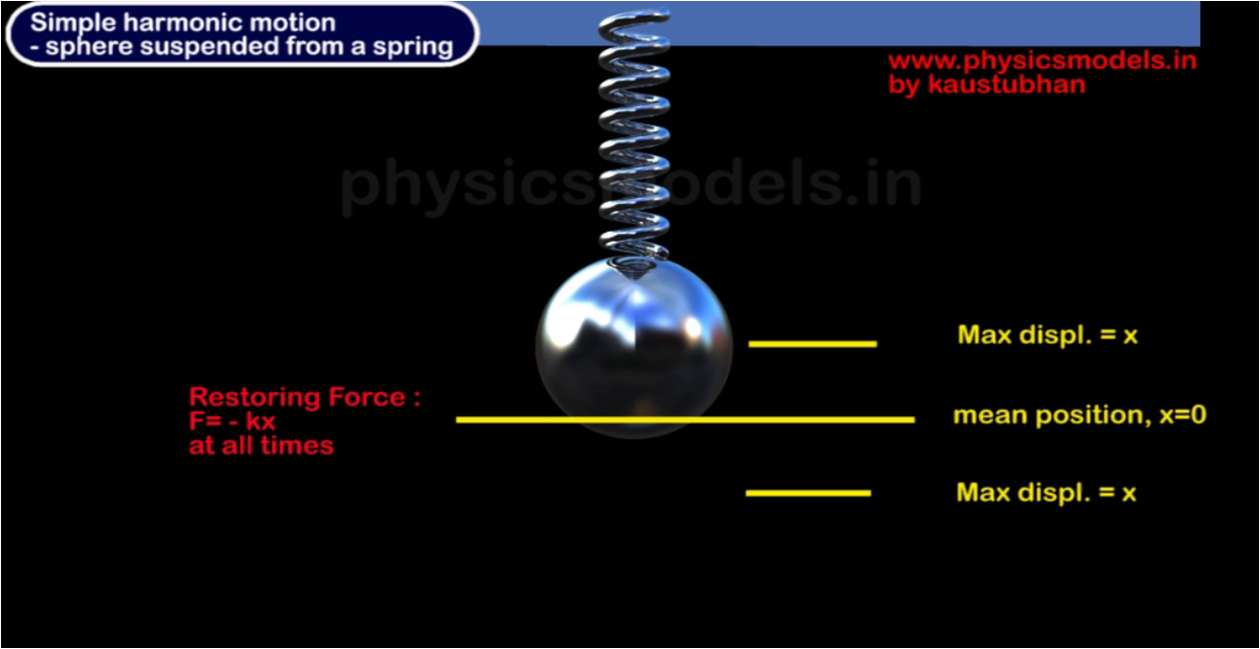
chapters
- PHYSICS FUNDAMENTALS(50)
- Previous Question Papers and Answers(1)
About Physicsmodels
This exciting learning content is brought to you by
KAD24 Teknosolutions
Private Limited, a startup established in 2017, having a passion for making physics attractive and not boring. The content has been carefully and meticulously designed with the help of physics teachers who understand what students need, their usual queries, and with an eye on tackling examinations too.
KAD24 Teknosolutions
(www.kad24.com)
does high-end engineering consulting, as Technical Advisors to the automotive companies on advanced cutting-edge technologies such as Electric Vehicles and Automotive Design in general.
APPRECIATION
AWARDS



Confused by physics? Need a rapid & effective guide for exams? Need solved problems explained? You have come to the right place
- We are a quality self-learning site. We build your confidence with our specially designed visuals
- Based on modern Learning Management System (LMS) backbone
- Modern approach to physics learning - Animations, Images, simplified explanations
- Compatible with mobile/laptop/desktop and Android, iOS devices
- Secure site with SSL certification + Data security
- We do not share customers data
- PayPal payment gateway (high security, efficient)
Sample Animations
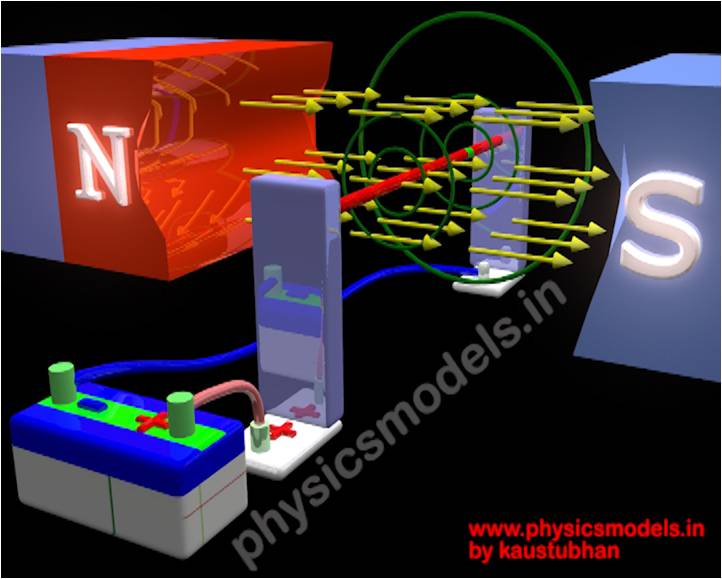
DC MOTOR
The D.C. Motor as a machine was a greatly useful invention, and it took in a Direct Current (DC) and churned out a rotating motion. Like a fan. Think of it as an ‘input-output machine’. DC means Direct Current, from a battery producing a constant voltage (which won’t be a sinusoidal wave like Alternating current). This Direct Current is the input into a conductor. A conductor can be any metallic piece. In a Motor, the metal is shapedlike a rectangle, running around a kind of boundary, and having a gap in the centre. What’s important is that the DC we feed in as input, should enter from one sideof the conductor...
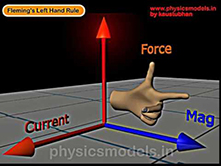
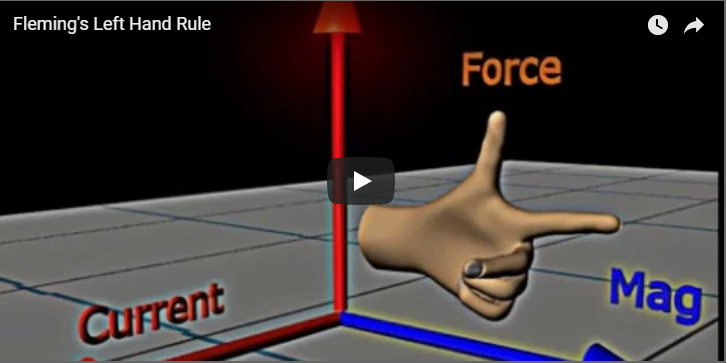
FLEMING'S LEFT HAND RULE
This rule connects three things :- 1) a magnetic field direction, 2) a current flow direction, 3) a Force direction on a conductor. The Fleming’s Left Hand Rule is about getting the right directions. In a situation where all these 3 things exist, the starting point is that you take your left Hand and then point precisely towards the direction of the magnetic field. 1. keep only your forefinger pointing in the direction of magnetic field. 2. turn your middle finger to point in the direction of current ....
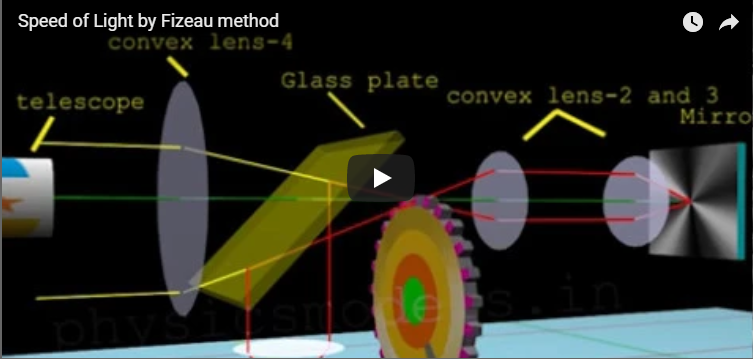
SPEED OF LIGHT
Light is really really fast, and a light beam travels at a velocity of 299792. 458 km/second. We can say it’s close to 300,000 km/second. The light from the sun reaches us after8 minutes and 20 seconds. This velocity is the same for every colour of light, violet to red, and hence is independent of wavelength or frequency. Measuring this kind of speed was a great challenge for scientists, at that time, using available technology of clocks to measure a time interval. Fizeau showed a brilliant method. He used an experimental setup which from one end to the other end needed 8.6 miles (13.84 km). That’s not much at all, considering that even...
Course Prices
Per Chapter US$1/- Only.. Validity-2 year..
Volume I US$24.99/- Only. Validity-2 years (1-22 Chapters)
Volume II US$24.99/- Only. Validity-2 years (23-47 Chapters)
Volume I & II US$39.99/- Only. Validity-2 years (47 Chapters)
NO. OF VIDEOS
NO. OF TOPICS
NO. OF SOLVED PROBLEMS
Test Questions
Appreciations